Understanding the Role of Cable Ties in Machine Wiring
Good cable management makes all the difference when it comes to how well industrial machines work and keeping workers safe. When wires are neatly arranged, there's less strain on the equipment itself, no unwanted electrical noise messing things up, and technicians can fix problems much faster than digging through a spaghetti mess. The numbers back this up too many factories report about 30 percent drop in electrical accidents after sorting out their wiring according to research from Industrial Safety Journal last year. Money talks here as well clean wiring saves companies cash by avoiding costly breakdowns while meeting those important safety regulations everyone has to follow.
The Importance of Cable Management in Industrial Machinery
When cables aren't properly organized, they create all sorts of problems including arc faults, short circuits, and damage caused by constant vibrations or friction against surfaces. This is especially bad news for big industrial equipment where slack wires might get caught in rotating parts, which can lead to complete system breakdowns at worst. Taking time to bundle cables together and secure them in place does more than just keep things neat it actually helps air circulate better around sensitive components. Better airflow means less heat buildup, something that matters a lot for machines working nonstop like those CNC units or robotic arms found in manufacturing plants across the country.
How Cable Ties Contribute to Securing Wires and Cables
Cable ties provide a cost-effective solution for immobilizing wire groups while accommodating natural thermal expansion. Their ribbed design ensures consistent tension, preventing slippage without crushing insulation. For corrosive environments, stainless steel or UV-resistant nylon variants maintain structural integrity under prolonged exposure to chemicals, moisture, or temperature fluctuations.
Applications of Cable Ties in Machine Wiring Across Industries
- Automotive: Securing sensor arrays and wiring harnesses in robotic assembly lines
- Energy: Bundling control cables in wind turbine nacelles exposed to salt spray and vibrations
-
Food Processing: Organizing washdown-rated equipment wiring using FDA-compliant ties
These examples highlight their versatility in balancing durability with precision across sectors.
Selecting the Right Cable Tie by Material, Size, and Environmental Resistance
Choosing cable ties based on size, color, and material
Select cable ties by first measuring the maximum bundle diameter of wires or cables. Standard widths range from 3.6 mm for small electronics to 19 mm for industrial machinery. Color selection serves dual purposes:
- Black ties for general use and UV protection
- Custom colors for safety compliance (red for emergency systems) or troubleshooting
Material choice directly impacts chemical resistance and lifespan. Nylon 6/6 (PA66) dominates industrial applications due to its flexibility and dielectric properties, while polyethylene suits short-term projects.
PA66 nylon and alternative materials for durability and chemical resistance
PA66 nylon withstands temperatures up to 185°F (85°C) and resists oils, fuels, and solvents a 2023 materials study showed 89% less degradation versus polypropylene in chemical-heavy environments. For extreme conditions:
| Material | Best For | Temperature Limit |
|---|---|---|
| PA66 Nylon | General industrial use | 185°F (85°C) |
| PVDF | High-purity chemical lines | 300°F (149°C) |
| PEEK | Aerospace components | 480°F (249°C) |
Heat-resistant and vibration-resistant cable ties for harsh industrial environments
In foundries or automotive plants, specify ties rated for continuous 250°F (121°C) operation with UL 94V-2 flame certification. Vibration-resistant models feature double-locking heads, serrated inner surfaces, and elongation limits below 2%. Leading manufacturers design these to withstand 15 G-force vibrations equivalent to heavy machinery operation.
Standard vs. steel-reinforced and tensioning steel cable ties: when to use each
Standard nylon ties work well in clean spaces where the weight stays below 50 pounds. For tougher jobs, there are steel reinforced versions that mix nylon covering with stainless steel inside. These stronger ties handle things like conveyor belts, telecom equipment outside, and those tight cables needing secure anchoring points. When dealing with really heavy tension situations, look at steel tensioning ties that can withstand over 1,200 Newtons or around 270 pounds before breaking. This extra strength keeps cables from slipping out of place, which is critical for sensor setups on bridges or in marine energy projects where failure isn't an option.
Best Practices for Installing Cable Ties in Machine Wiring
Step-by-Step Guide to Proper Cable Tie Installation
Start sorting those cables into groups that make sense for what they do or where they go. Take a cable tie and wrap it around the bunch, making sure the end goes all the way through the locking part. Gently pull until it sits tight against the wires but don't force it suddenly because that can mess up how evenly everything is held together. Cut off any extra length at about a 45 degree angle so there aren't any pointy bits sticking out. If working somewhere with lots of vibrations, remember to leave about 3 to 5 millimeters of the tail hanging free. This little bit of slack lets things move naturally without breaking the hold.
How to Secure Cables Without Damaging Insulation
When installing cable ties, go for ones with smooth edges and rounded heads since they create fewer pressure points on the cables. Don't just snap them tight all at once either. Over tightening is a common mistake that actually squishes the insulation material by around 30% in some cases, which raises the risk of shorts happening down the line. For areas where wires might be stressed or moving around, it's worth adding some protection like sleeves or spiral wraps right at those contact spots. And if dealing with really important wiring systems, invest in those special tension limiting tools that shut off when reaching about 8 to 12 pounds of force. Most industrial cables handle well within this range, so these tools help prevent damage while still keeping everything secure enough.
Optimal Spacing and Placement of Cable Ties Along Wiring Runs
- Horizontal runs: Space ties 12–18" apart
- Vertical runs: Place ties every 6–12" to prevent sagging
-
Bends/transitions: Install ties within 1" of directional changes
Always align locking mechanisms on the less visible side for easier inspection. In EMI-sensitive areas, maintain 2" clearance between cable ties and signal-carrying conductors.
Avoiding Over-Tightening to Maintain Wire Flexibility and Reduce Stress
The "finger twist test" remains the gold standard—if you can rotate the tie 15–20° with moderate finger pressure, tension is adequate. Over-compressed bundles show 43% higher failure rates in thermal cycling tests (materials research 2022). For temperature-sensitive environments, leave expansion loops near each tie to accommodate material contraction and expansion.
Mounting and Securing Cable Ties for Long-Term Stability
Screw Mount vs. Push Mount: Selecting the Right Attachment Method
When it comes to keeping things secure long term, screw mounted cable ties really stand out because they attach directly to equipment panels using actual machine screws or bolts. They work great in those tough spots where vibrations are constant, such as around CNC machines, since regular ties would just come loose and wires could fall out completely. For situations that need quick fixes or adjustments on site, push mounts are the way to go. These have little plastic parts that snap right into existing holes without needing any tools at all. According to recent data from industrial maintenance folks in 2023, most big machinery still relies heavily on screw mounts about 78% of the time. Meanwhile, lighter duty setups like robotic arms that get changed around often tend to favor push mounts instead.
Using Adhesive-Backed Mounts and Integrated Brackets in Equipment Design
Mounting bases with adhesive backing make installation quick and easy on smooth surfaces such as control panels and conveyor housing units. The acrylic adhesives used are pretty strong stuff too, holding up against heat as high as 90 degrees Celsius which translates to around 194 Fahrenheit. That makes these bases work well inside machines where there isn't much space for regular mounting options. Many modern designs include built-in brackets right in the motor housing or sensor setup, so technicians can thread cables through directly without needing extra clips or screws. Some top companies have started putting UV resistant nylon mounts into their outdoor gear lately. Field workers report cutting down installation time by about a third when using these new mounting solutions instead of older techniques.
Ensuring Reliability Under Vibration: Insights from Automotive Manufacturing
The automotive manufacturing world really needs solutions that can stand up to constant vibrations because loose wiring is responsible for around 12% of all electrical problems each year. Many top tier suppliers have started combining stainless steel cable ties with those special anti-slip pads inside engine areas to combat the annoying slippage caused by resonance. Take Toyota for instance their 2022 report showed something interesting about this topic they saw about a 40% drop in failed cable ties once they started using these staggered mounting setups along with those tamper proof locking heads on their robot welders. From what most experienced technicians will tell you, it's generally wise to space out those mounting points no more than 300 mm apart when dealing with vibrating conveyor belts, and definitely go for dual tab bases whenever handling important power connections throughout the plant.
Optimizing Cable Organization for Safety, Maintenance, and Efficiency
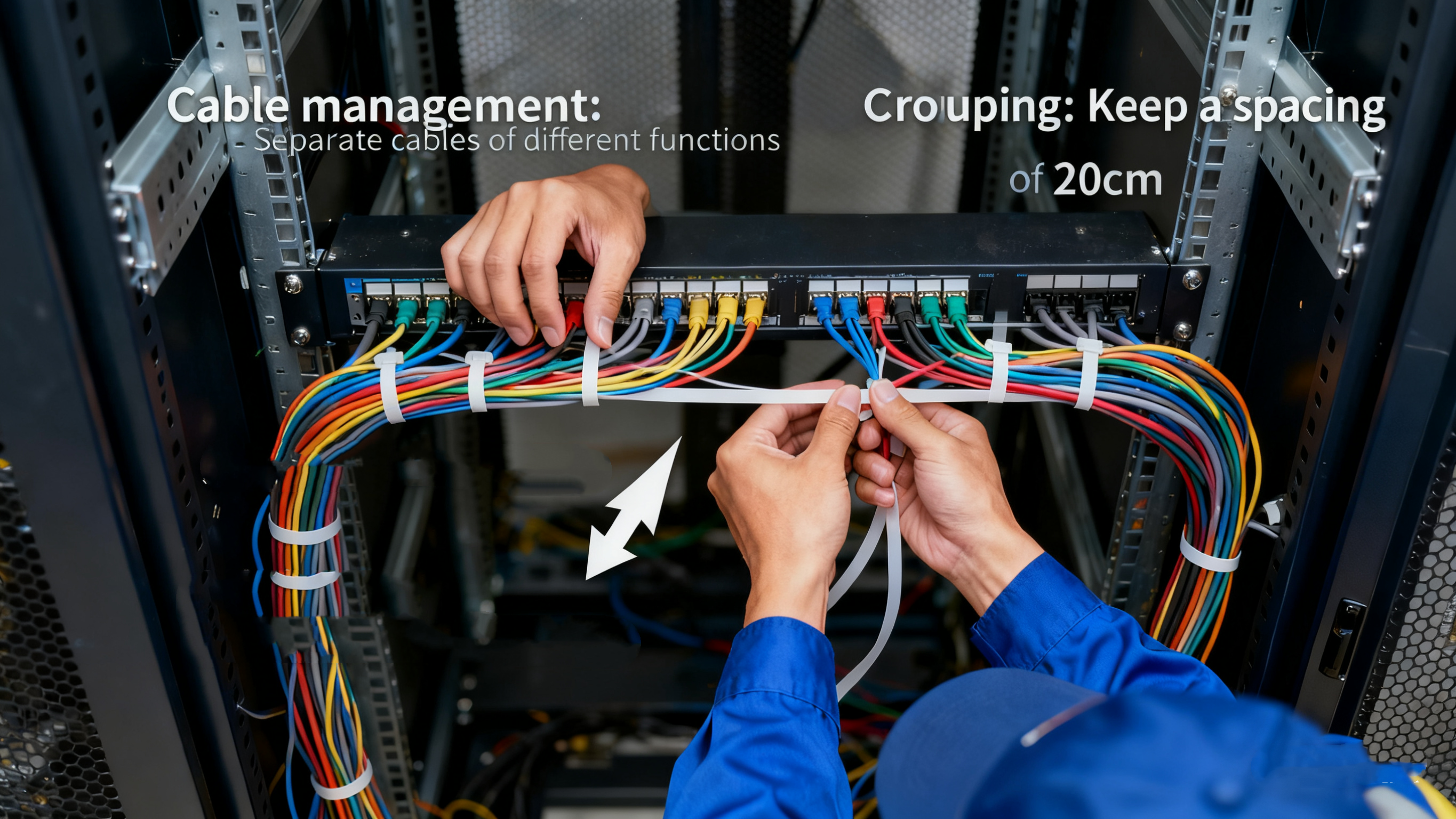
Strategic Cable Routing and Grouping by Function for Clarity
Organizing cables according to their functions with cable ties makes life much easier when something goes wrong or needs regular maintenance on machinery. When power cords, control wires, and data lines are grouped separately, electricians spend less time hunting around for particular circuits during inspections. According to recent research from Electrical Safety Journal back in 2023, this approach cuts down cable tangle problems by nearly two thirds in factory control panels. Plus, it keeps everything looking neat and orderly, which matters because most industrial facilities still need to follow those NFPA 79 guidelines for proper wiring arrangements anyway.
Separating Power, Signal, and Data Lines to Minimize Interference
Maintain 3" spacing between high-voltage power cables and low-voltage signal lines using dedicated cable ties to prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI). Nylon cable ties with ultraviolet resistance are ideal for securing shielded data cables in robotic arms and CNC machines, preserving signal integrity in 480V manufacturing environments.
Using Color-Coded Cable Ties for Quick Identification and Troubleshooting
Adopt industry-standard color coding:
- Red: Emergency stop circuits
- Yellow: Hydraulic/pneumatic control signals
-
Blue: Ethernet/Fieldbus networks
A Tier 1 automotive supplier reduced electrical diagnostic time by 35% after implementing this system with UV-stable cable ties.
Enhancing Electrical Safety and Reducing Maintenance Time with Organized Wiring
Properly tensioned cable ties prevent abrasive contact between wires and sharp machine edges, a leading cause of insulation failure. Facilities using ladder racks with spaced cable tie mounts report 28% fewer arc-flash incidents compared to traditional wire channel installations.
Case Study: Reducing Downtime in Manufacturing Through Optimized Cable Management
A food processing plant eliminated 12 hours/month of unplanned downtime by reorganizing 1,200+ cables in packaging machinery with heat-resistant cable ties and modular mounting plates. Technicians now complete motor replacements 45% faster due to clearly labeled power groups and separation of steam-resistant sensor lines.
FAQ Section
Why are cable ties essential in industrial machine wiring?
Cable ties are crucial for organizing and securing wires in industrial machines, preventing damage from vibrations and friction, enhancing airflow, and ensuring a safer working environment.
What materials are best for cable ties in harsh industrial environments?
PA66 Nylon, PVDF, and PEEK are recommended materials for cable ties in harsh environments due to their temperature resistance and chemical durability.
How should cable ties be installed to avoid damaging insulation?
Cable ties should be installed with smooth edges and rounded heads, not over-tightened, and with protective sleeves or wraps in areas of stress or movement.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Role of Cable Ties in Machine Wiring
- Selecting the Right Cable Tie by Material, Size, and Environmental Resistance
- Best Practices for Installing Cable Ties in Machine Wiring
- Mounting and Securing Cable Ties for Long-Term Stability
- Using Adhesive-Backed Mounts and Integrated Brackets in Equipment Design
- Ensuring Reliability Under Vibration: Insights from Automotive Manufacturing
- Optimizing Cable Organization for Safety, Maintenance, and Efficiency
- Case Study: Reducing Downtime in Manufacturing Through Optimized Cable Management
- FAQ Section